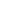
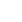
Caernarfon Castle (Welsh: Castell Caernarfon) is a medieval fortress in Caernarfon, Gwynedd, north-west Wales cared for by Cadw, the Welsh Government's historic environment service. There was a motte-and-bailey castle in the town of Caernarfon from the late 11th century until 1283 when King Edward I of England began replacing it with the current stone structure. The Edwardian town and castle acted as the administrative centre of north Wales and as a result the defences were built on a grand scale. There was a deliberate link with Caernarfon's Roman past and the Roman fort of Segontium is nearby.
While the castle was under construction, town walls were built around Caernarfon. The work cost between £20,000 and £25,000 from the start until the end of work in 1330. Despite Caernarfon Castle's external appearance of being mostly complete, the interior buildings no longer survive and many of the building plans were never finished. The town and castle were sacked in 1294 when Madog ap Llywelyn led a rebellion against the English. Caernarfon was recaptured the following year. During the Glyndŵr Rising of 1400–1415, the castle was besieged. When the Tudor dynasty ascended to the English throne in 1485, tensions between the Welsh and English began to diminish and castles were considered less important. As a result, Caernarfon Castle was allowed to fall into a state of disrepair.
Despite its dilapidated condition, during the English Civil War Caernarfon Castle was held by Royalists, and was besieged three times by Parliamentarian forces. This was the last time the castle was used in war. Caernarfon Castle was neglected until the 19th century when the state funded repairs. In 1911, Caernarfon Castle was used for the investiture of the Prince of Wales, and again in 1969. It is part of the World Heritage Site "Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd".
Later history
For around two centuries after the conquest of Wales, the arrangements established by Edward I for the governance of the country remained in place. During this time the castle was constantly garrisoned, and Caernarfon was effectively the capital of north Wales. There was a degree of discrimination, with the most important administrative jobs in Wales usually closed to Welsh people. Tension between the Welsh and their English conquerors spilled over at the start of the 15th century with the outbreak of the Glyndŵr Rising (1400–1415). During the revolt, Caernarfon was one of the targets of Owain Glyndŵr's army. The town and castle were besieged in 1401, and in November that year the Battle of Tuthill took place nearby between Caernarfon's defenders and the besieging force. In 1403 and 1404, Caernarfon was besieged by Welsh troops with support from French forces; the garrison at the time was around thirty. The ascension of the Tudor dynasty to the English throne in 1485 heralded a change in the way Wales was administered. The Tudors were Welsh in origin, and their rule eased hostilities between the Welsh and English. As a result, castles such as Caernarfon, which provided secure centres from which the country could be administered, became less important. They were neglected, and in 1538 it was reported that many castles in Wales were "moche ruynous and ferre in decaye for lakke of tymely reparations".
In Caernarfon's case the walls of the town and castle remained in good condition, while features which required maintenance – such as roofs – were in a state of decay and much timber was rotten. Conditions were so poor that of the castles seven towers and two gatehouses, only the Eagle Tower and the King's Gate had roofs by 1620. The domestic buildings inside the castle had been stripped of anything valuable, such as glass and iron. Despite the disrepair of the domestic buildings, the castle's defences were in a good enough state that during the English Civil War in the mid-17th century it was garrisoned by Royalists. Caernarfon Castle was besieged three times during the war. The constable was John Byron, 1st Baron Byron, who surrendered Caernarfon to Parliamentarian forces in 1646. It was the last time Caernarfon Castle saw fighting. Although it was ordered in 1660 that the castle and town walls should be dismantled, the work was aborted early on and may never have started.
Despite avoiding slighting, the castle was neglected until the late 19th century. From the 1870s onwards, the government funded repairs to Caernarfon Castle. The deputy-constable, Llewellyn Turner oversaw the work, in many cases controversially restoring and rebuilding the castle, rather than simply conserving the existing stonework. Steps, battlements, and roofs were repaired, and the moat to the north of the castle was cleared of post-medieval buildings that were considered to spoil the view, despite the protest of locals. Under the auspices of the Office of Works and its successors since 1908, the castle was preserved due to its historic significance. In 1911, Caernarfon was used for the investiture of the Prince of Wales for the first time when Prince Edward (later Edward VIII), eldest son of the newly crowned King George V; the ceremony was held there at the insistence of then-Chancellor of the Exchequer David Lloyd George, a Welshman raised in Caernarfonshire. In 1969, the precedent was repeated with the investiture of Charles, Prince of Wales. Although Caernarfon Castle has been the property of the Crown since it was built, it is currently cared for by Cadw (English: to keep), the Welsh Government's historic environment division, responsible for the maintenance and care of Wales' historic buildings. In 1986, Caernarfon was added to the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites as part of the "Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd" in recognition of its global importance and to help conserve and protect the site. The castle houses the Royal Welch Fusiliers Museum. During 2015 a new "entrance pavilion" was built, designed by architects Donald Insall Associates.
Architecture
Caernarfon Castle's design was partly influenced by a desire to make the structure impressive as a symbol of the new English rule in Wales. This was particularly acute as Caernarfon was made the centre of government in the northern part of the country. The Edwardian castle's layout was mostly dictated by the lay of the land, although the inclusion of the previous castle's motte played a part. It is a narrow enclosure, roughly in the shape of a figure eight. It was divided into two enclosures, upper and lower "wards" in the east and west respectively, with the eastern containing royal accommodation, although this was never completed. The divide was supposed to be established by a range of fortified buildings, however these too were never built.
Studded along the curtain wall are several polygonal towers from which flanking fire could be deployed. There were battlements on the tops of walls and towers, and along the southern face were firing galleries; it was intended to included galleries along the northern face but they were never built. In the opinion of military historian Allen Brown, this combined to make Caernarfon Castle "one of the most formidable concentrations of fire-power to be found in the Middle Ages". Most of the northern towers stand had four-storeys including a basements. The Eagle Tower at the western corner of the castle was the grandest. It has three turrets which were once surmounted by statues of eagles. The tower contained grand lodgings, and was probably built for Sir Otton de Grandson, the first justiciar of Wales. A basement level contained a water gate, through which visitors travelling up the River Seiont could enter the castle. Water was drawn from a well in the eponymous Well Tower.
Caernarfon's appearance differs from that of other Edwardian castles through the use of banded coloured stone in the walls and in its polygonal, rather than round, towers. There has been extensive academic debate over the interpretation of these features. Historian Arnold Taylor argued that the design of the castle was a representation of the Walls of Constantinople. The conscious use of imagery from the Byzantine Roman Empire was therefore an assertion of authority by Edward I, and influenced by the legendary dream of Magnus Maximus, a Roman emperor. In his dream Maximus had seen a fort, "the fairest that man ever saw", within a city at the mouth of a river in a mountainous country and opposite an island. Edward interpreted this to mean Segontium was the city of Maximus' dream and drew on the imperial link when building Caernarfon Castle. Recent work by historian Abigail Wheatley suggests that the design of Caernarfon was indeed an assertion of Edward's authority, but that it drew on imagery from Roman sites in Britain with the intent of creating an allusion of Arthurian legitimacy for the king.
There were two main entrances, one leading from the town (the King's Gate) and one allowing direct access to the castle without having to proceed through the town (the Queen's Gate). Their form was typical of the time – a passage between two flanking towers. If the King's Gate had been completed, a visitor would have crossed two drawbridges, passed through five doors, under six portcullises, and negotiated a right-angle turn before emerging into the lower enclosure. The route was overlooked by numerous arrow loops and murder holes. A statue of Edward II was erected in a niche overlooking the town, above the entrance to the King's Gate. In the opinion of architectural historian Arnold Taylor, "No building in Britain demonstrates more strikingly the immense strength of medieval fortifications than the great twin-towered gateway to Caernarfon Castle." The Queen's Gate is unusual in that its entrance is above ground level; this was due to the integration of the earlier motte, raising the ground level of the interior. Externally, the gate would have been approached by a stone ramp which is no longer present.
While the curtain wall and its towers survive largely intact, all that remains of the buildings contained within the castle are the foundations. While royal lodgings were in the upper ward, the lower contained buildings such as the kitchens. The kitchens were located immediately west of the King's Gate. On the basis of their insubstantial foundations, Taylor suggests that the kitchens were not strongly built. The other key feature of the castle's domestic side, was the Great Hall. Caernarfon's abutted the south side of the lower ward and was 30.5 metres (100 ft). Though only the foundations survive, in its heyday the Great Hall would have been an impressive building, featuring fine architecture, and used to host royal entertainment. Had Caernarfon been completed as intended, it would have been able to contain a royal household of several hundred people.