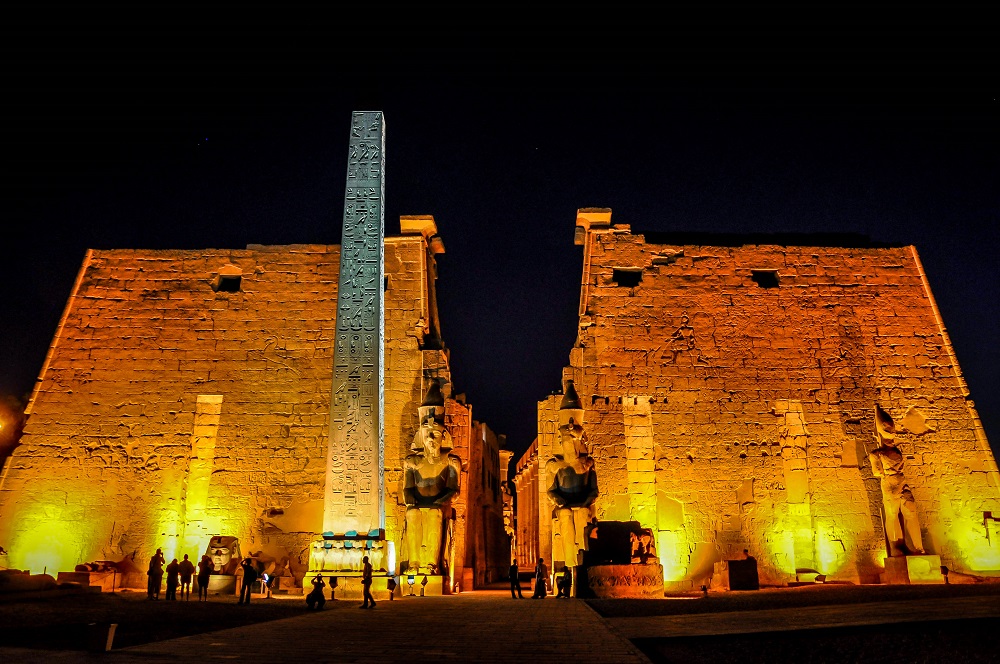
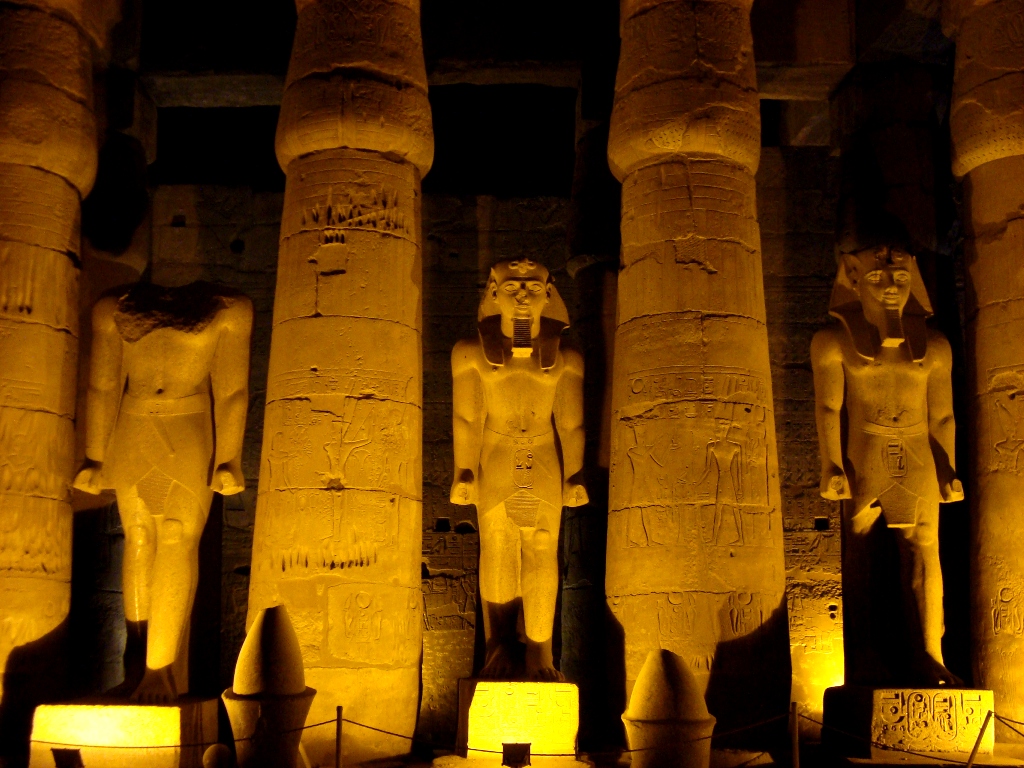
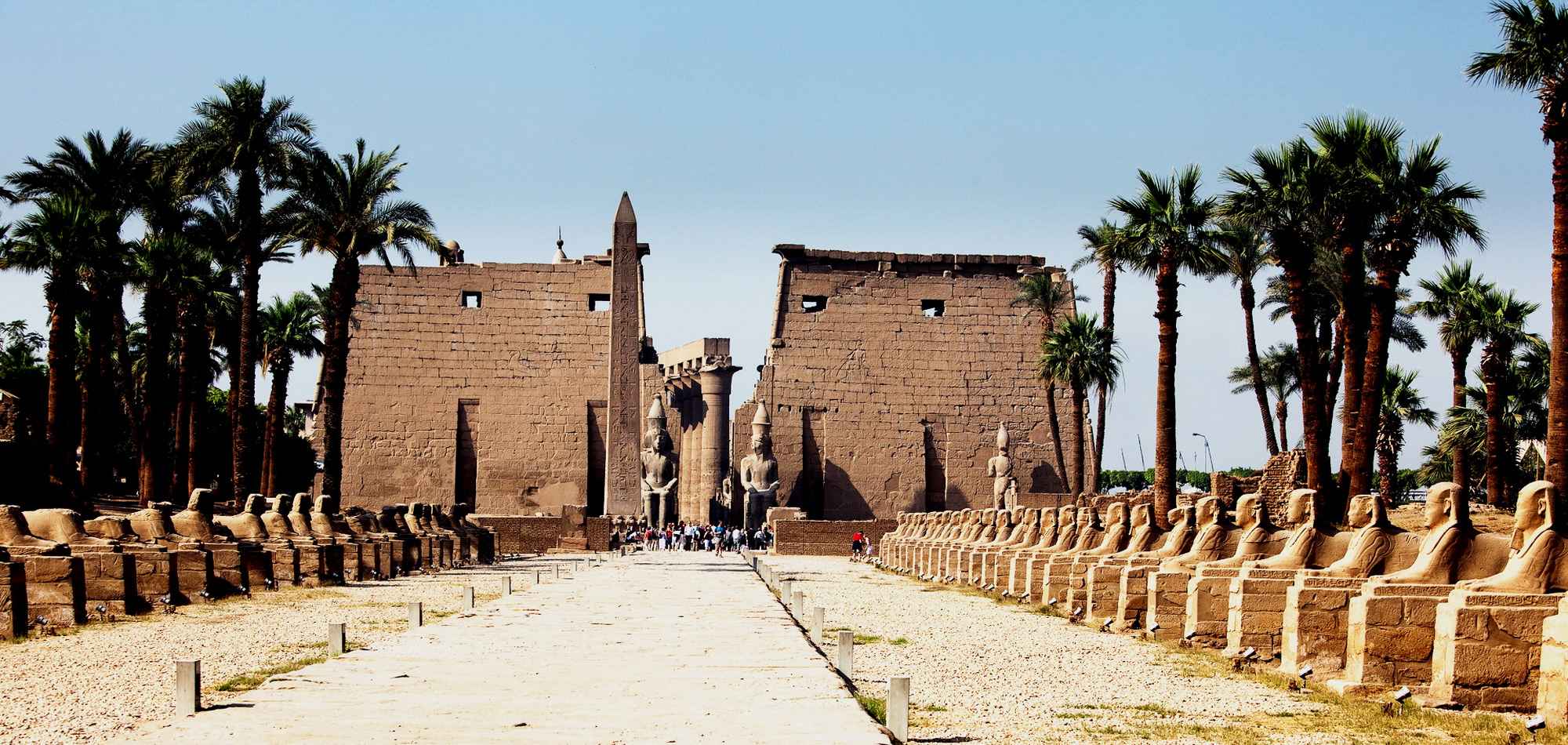
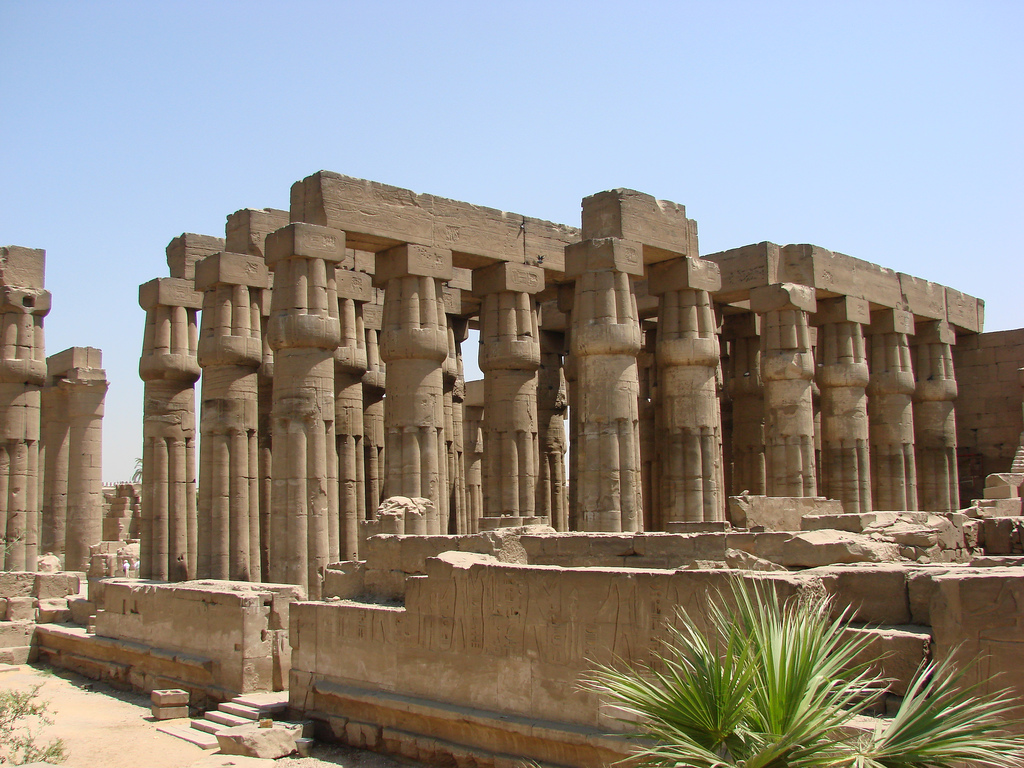
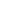
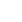
Luxor Temple is a large Ancient Egyptian temple complex located on the east bank of the Nile River in the city today known as Luxor (ancient Thebes) and was founded in 1400 BCE. Known in the Egyptian language as ipet resyt, or "the southern sanctuary". In Luxor there are six great temples, the four on the left bank are known to travellers and readers of travels as Goornah, Deir-el-Bahri, the Ramesseum, and Medinet Habu; and the two temples on the right bank are known as the Karnak and Luxor.
To the rear of the temple are chapels built by Tuthmosis III, and Alexander. During the Roman era, the temple and its surroundings were a legionary fortress and the home of the Roman government in the area.
The Luxor temple was built with sandstone from the Gebel el-Silsila area, which is located in south-western Egypt. This sandstone from the Gebel el-Silsila region is referred to as Nubian Sandstone. This sandstone was used for the construction for monuments in Upper Egypt as well as in the course of past and current restoration works.
Like other Egyptian structures a common technique used was symbolism, or illusionism. For example, to the Egyptian, a sanctuary shaped like an Anubis Jackal was really Anubis. At the Luxor temple, the two obelisks (the smaller one closer to the west is now in the Place de la Concorde in Paris) flanking the entrance were not the same height, but they created the illusion that they were. With the layout of the temple they appear to be of equal height, but using illusionism, it enhances the relative distances hence making them look the same size to the wall behind it. Symbolically, it is a visual and spacial effect to emphasize the heights and distance from the wall, enhancing the already existing pathway.
From medieval times the Muslim population of Luxor had settled in and around the temple, at the southward end of the mount. Due to the Luxor’s past city population building on top of and around the Luxor temple, centuries of rubble had accumulated, to the point where there was an artificial hill some forty-eight or fifty feet in height. The Luxor Temple had begun to be excavated by Professor Gaston Maspero after 1884 after he had been given the order to commence operations. The excavations were carried out sporadically until 1960. Over time, accumulated rubbish of the ages had buried three quarters of the temple which contained the courts and colonnades which formed the nucleus of the Arab half of the Modern village. Maspero had taken an interest earlier, and he had taken over the post of Mariette Pasha to complete the job in 1881. Not only was there rubbish, but there was also barracks, stores, houses, huts, pigeon towers, which needed to be removed in order to excavate the site. Maspero received from the Egyptian minister of public works the authorization needed to obtain funds in order to negotiate compensation for the pieces of land covered by the houses and dependencies.