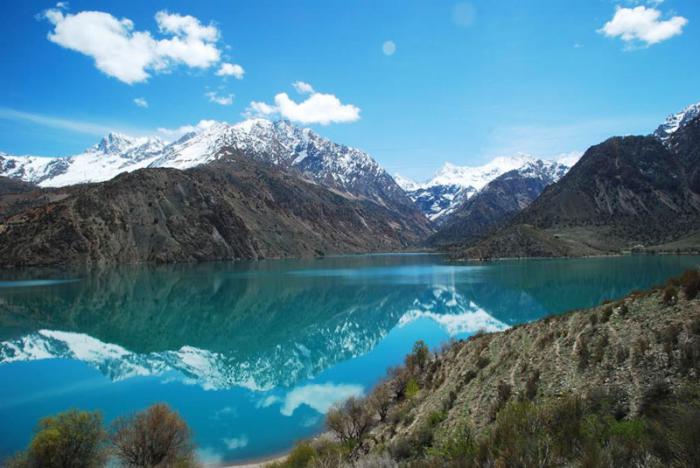
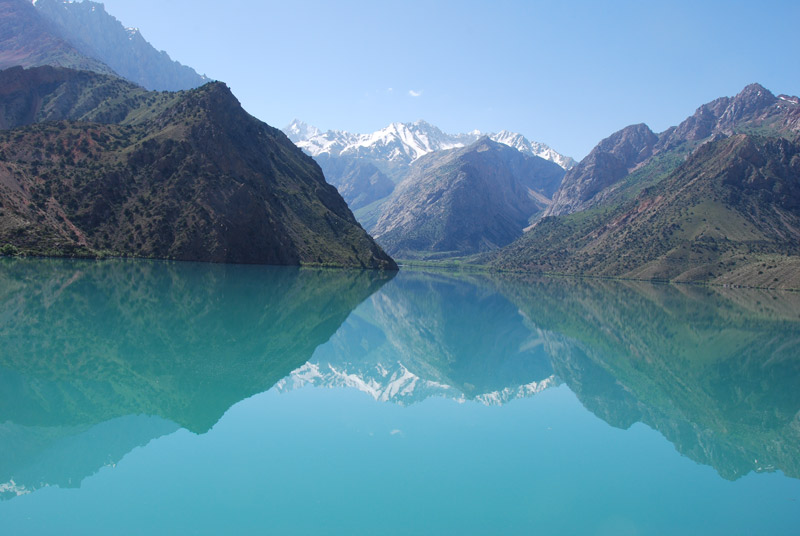
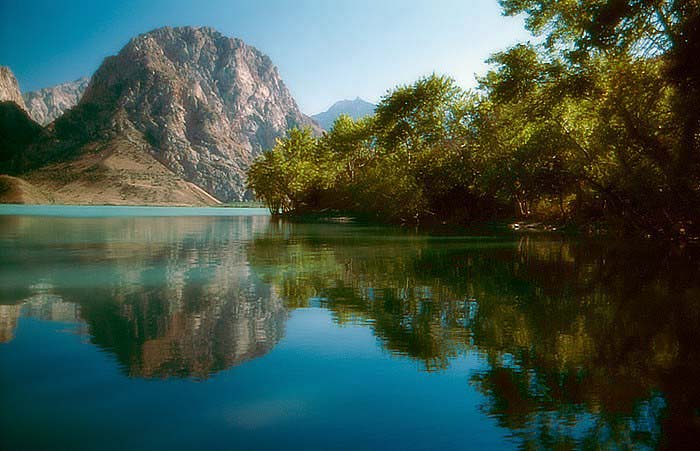
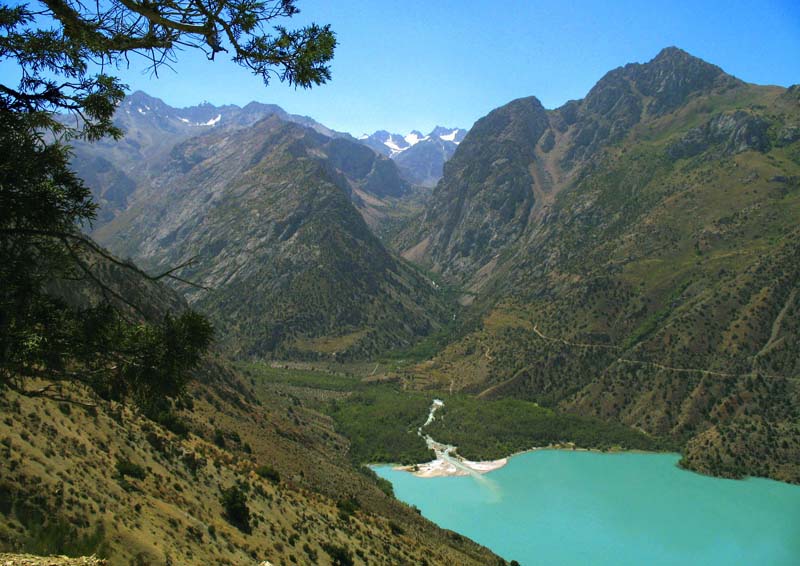
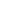
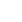
Iskanderkul is a mountain lake of glacial origin in Tajikistan's Sughd Province. It lies at an altitude of 2,195 metres (7,201 ft) on the northern slopes of the Gissar Range in the Fann Mountains. Triangular in shape, it has a surface area of 3.4 square kilometres (1.3 sq mi) and is up to 72 metres (236 ft) deep. Claimed to be one of the most beautiful mountain lakes in the former Soviet Union, it is a popular tourist destination.
It was formed by the congestion of the Saratogh river. It is 134 km from Dushanbe and 23 km from the Dushanbe—Khujand road.
The lake takes its name from Alexander the Great: Iskander is the Persian pronunciation of Alexander, and kul is lake in Tajik, which is of Turkic origin.
The outflow of the lake is the Iskander Darya, which joins the Yaghnob River to form the Fan Darya, a major left tributary of the Zeravshan River.
A 300 square kilometres (120 sq mi) tract of land including the lake and surrounding mountains has been designated a nature reserve. As well as the lake itself, habitats found in the reserve include rivers, water meadows, broad-leaved and juniper forests, mountain shrubland and sub-alpine meadows. Over half of the reserve, comprising 177 square kilometres (68 sq mi), has been identified by BirdLife International as an Important Bird Area because it supports significant numbers of the populations of various bird species, either as residents, or as breeding or passage migrants. These include Himalayan snowcocks, saker falcons, cinereous vultures, yellow-billed choughs, Hume's larks, sulphur-bellied warblers, wallcreepers, white-tailed rubythroats, white-winged redstarts, white-winged snowfinches, alpine accentors, rufous-streaked accentors, brown accentors, water pipits, fire-fronted serins, plain mountain-finches, crimson-winged finches, red-mantled rosefinches and white-winged grosbeaks