Although the term "Blue Ridge" is sometimes applied exclusively to the eastern edge or front range of the Appalachian Mountains, the geological definition of the Blue Ridge province extends westward to the Ridge and Valley area, encompassing the Great Smoky Mountains, the Great Balsams, the Roans, the Blacks, the Brushy Mountains (a "spur" of the Blue Ridge) and other mountain ranges.
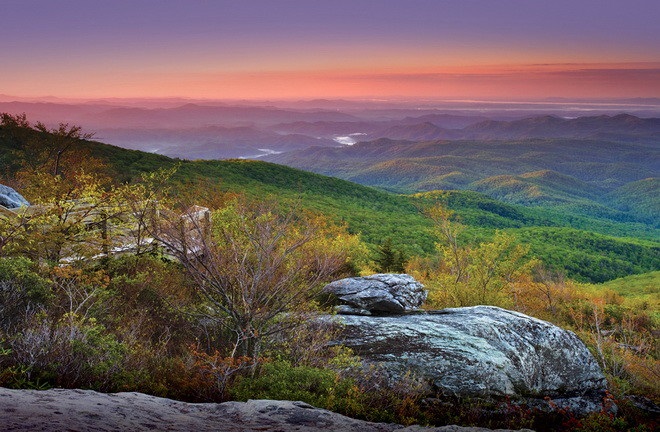
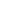
The Blue Ridge Mountains as seen from Blowing Rock, North Carolina.
The Blue Ridge extends as far north into Pennsylvania as South Mountain. While South Mountain dwindles to mere hills between Gettysburg and Harrisburg, the band of ancient rocks that forms the core of the Blue Ridge continues northeast through the New Jersey and Hudson River highlands, eventually reaching The Berkshires of Massachusetts and the Green Mountains of Vermont.
The Blue Ridge contains the highest mountains in eastern North America south of Baffin Island. About 125 peaks exceed 5,000 feet (1,500 m) in elevation.[5] The highest peak in the Blue Ridge (and in the entire Appalachian chain) is Mt. Mitchell in North Carolina at 6,684 feet (2,037 m). There are 39 peaks in North Carolina and Tennessee higher than 6,000 feet (1,800 m); by comparison, in the northern portion of the Appalachian chain only New Hampshire's Mt. Washington rises above 6,000 feet. Southern Sixers is a term used by peak baggers for this group of mountains.[6]
The Blue Ridge Parkway runs 469 miles (755 km) along crests of the Southern Appalachians and links two national parks: Shenandoah and Great Smoky Mountains. In many places along the parkway, there are metamorphic rocks (gneiss) with folded bands of light-and dark-colored minerals, which sometimes look like the folds and swirls in a marble cake.