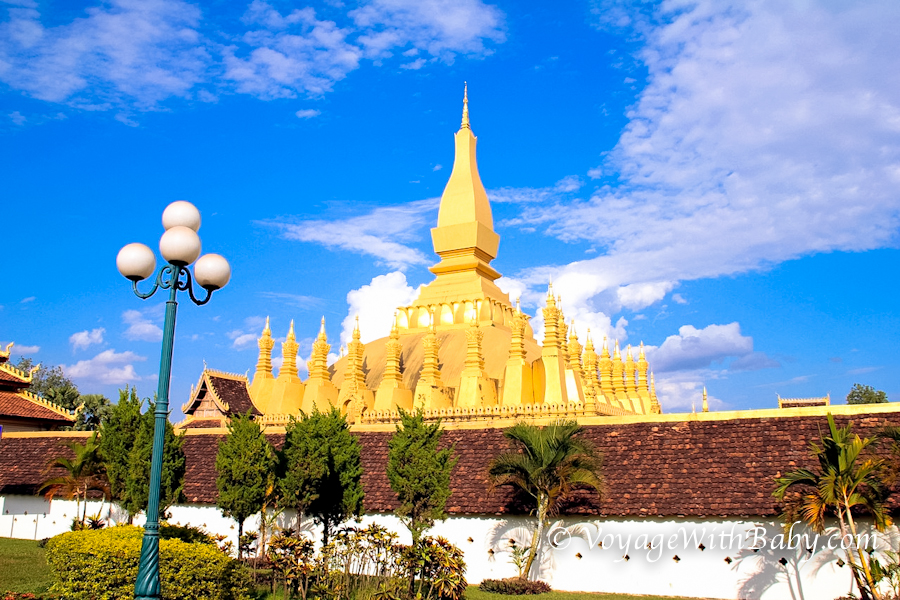
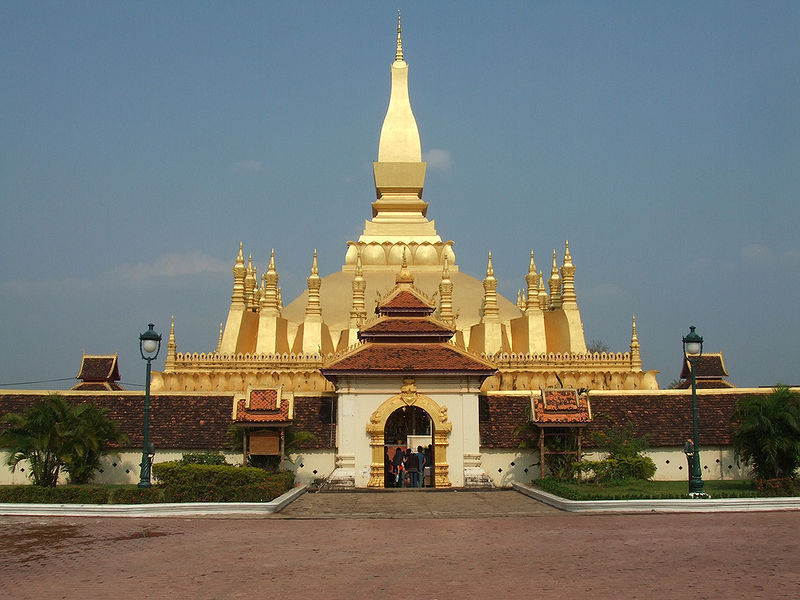
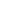
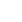
Pha That Luang (Lao: ພຣະທາດຫຼວງ, IPA: [pʰā tʰâːt lwǎːŋ] 'Great Stupa') is a gold-covered large Buddhist stupa in the centre of Vientiane, Laos. Since its initial establishment, suggested to be in the 3rd century, the stupa has undergone several reconstructions as recently as the 1930s due to foreign invasions of the area. It is generally regarded as the most important national monument in Laos and a national symbol.
Pha That Luang according to the Lao people was originally built as a Hindu temple in the 3rd century. Buddhist missionaries from the Mauryan Empire are believed to have been sent by the Emperor Ashoka, including Bury Chan or Praya Chanthabury Pasithisak and five Arahata monks who brought a holy relic (believed to be the breastbone) of Lord Buddha to the stupa. It was rebuilt in the 13th century as a Khmer temple which fell into ruin.
In the mid-16th century, King Setthathirat relocated his capital from Luang Prabang to Vientiane and ordered construction of Pha That Luang in 1566. It was rebuilt about 4 km from the centre of Vientiane at the end of That Luang Road and named Pha That Luang. The bases had a length of 69 metres each and was 45 metres high, and was surrounded by 30 small Stupas.
In 1641, a Dutch envoy of the Dutch East India Company, Gerrit van Wuysoff, visited Vientiane and was received by King Sourigna Vongsa at the temple, where he was, reportedly, received in a magnificent ceremony. He wrote that he was particularly impressed by the "enormous pyramid and the top was covered with gold leaf weighing about a thousand pounds". However, the stupa was repeatedly plundered by the Burmese, Siamese and Chinese.
Pha That Luang was destroyed by the Thai invasion in 1828, which left it heavily damaged and abandoned. It was not until 1900 that the French restored to its original design based on the detailed drawings from 1867 by the French architect and explorer Louis Delaporte. However the first attempt to restore it was unsuccessful and it had to be redesigned and then reconstructed in the 1930s. During the Franco-Thai War, Pha That Luang was heavily damaged during a Thai air raid. After the end of World War II, Pha That Luang was reconstructed.
The architecture of the building includes many references to Lao culture and identity, and so has become a symbol of Lao nationalism. The stupa today consists of three levels, each conveying a reflection of part of the Buddhist doctrine. The first level is 223 feet (67 metres) by 226 feet (68 metres), the second is 157 feet (47 metres) along each side and the third level is 98 feet (29 metres) along each side. From ground to pinniacle, Pha That Luang is 147.6 feet (44 metres) high.
The area around Pha That Luang is now gated, to keep traffic out. Previously visitors could drive around the whole complex. The encircling walls are roughly 279 feet (85 metres) long on each side and contain a large number of Lao and Khmer sculptures including one of Jayavarman VII.