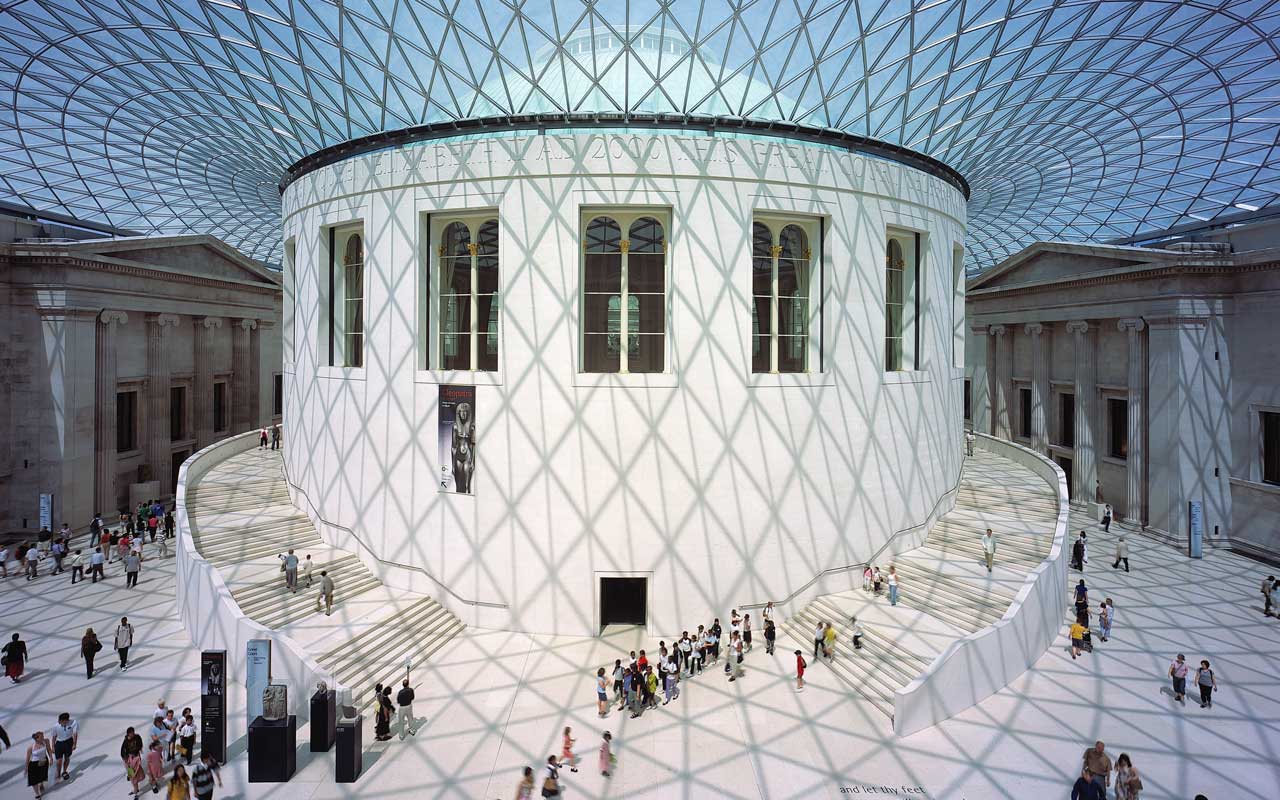
The British Museum is a museum dedicated to human history, art, and culture, located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection, numbering some 8 million works, is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence and originates from all continents, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present.
The British Museum was established in 1753, largely based on the collections of the physician and scientist Sir Hans Sloane. The museum first opened to the public on 15 January 1759, in Montagu House in Bloomsbury, on the site of the current museum building. Its expansion over the following two and a half centuries was largely a result of an expanding British colonial footprint and has resulted in the creation of several branch institutions, the first being the British Museum (Natural History) in South Kensington in 1881. Some objects in the collection, most notably the Elgin Marbles from the Parthenon, are the objects of controversy and of calls for restitution to their countries of origin.
Until 1997, when the British Library (previously centred on the Round Reading Room) moved to a new site, the British Museum housed both a national museum of antiquities and a national library in the same building. The museum is a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport, and as with all other national museums in the United Kingdom it charges no admission fee, except for loan exhibitions. Neil MacGregor became director of the museum in August 2002, succeeding Robert G. W. Anderson. In April 2015, MacGregor announced that he would step-down as Director on 15 December. On 29 September 2015, the Board of Trustees confirmed Hartwig Fischer, who will assume his post in Spring 2016, as his successor.
History
Hans Sloane, founder of the British Museum
Although today principally a museum of cultural art objects and antiquities, the British Museum was founded as a "universal museum". Its foundations lie in the will of the Irish-born British physician and naturalist Sir Hans Sloane (1660–1753). During the course of his lifetime Sloane gathered an enviable collection of curiosities and, not wishing to see his collection broken up after death, he bequeathed it to King George II, for the nation, for a sum of £20,000.
At that time, Sloane's collection consisted of around 71,000 objects of all kinds including some 40,000 printed books, 7,000 manuscripts, extensive natural history specimens including 337 volumes of dried plants, prints and drawings including those by Albrecht Dürer and antiquities from Sudan, Egypt, Greece, Rome, the Ancient Near and Far East and the Americas.
The British Museum today
Today the museum no longer houses collections of natural history, and the books and manuscripts it once held now form part of the independent British Library. The Museum nevertheless preserves its universality in its collections of artefacts representing the cultures of the world, ancient and modern. The original 1753 collection has grown to over thirteen million objects at the British Museum, 70 million at the Natural History Museum and 150 million at the British Library.
The Round Reading Room, which was designed by the architect Sydney Smirke, opened in 1857. For almost 150 years researchers came here to consult the Museum's vast library. The Reading Room closed in 1997 when the national library (the British Library) moved to a new building at St Pancras. Today it has been transformed into the Walter and Leonore Annenberg Centre.
With the bookstacks in the central courtyard of the museum empty, the process of demolition for Lord Foster's glass-roofed Great Court could begin. The Great Court, opened in 2000, while undoubtedly improving circulation around the museum, was criticised for having a lack of exhibition space at a time when the museum was in serious financial difficulties and many galleries were closed to the public. At the same time the African collections that had been temporarily housed in 6 Burlington Gardens were given a new gallery in the North Wing funded by the Sainsbury family – with the donation valued at £25 million.
As part of its very large website, the museum has the largest online database of objects in the collection of any museum in the world, with 2,000,000 individual object entries, 650,000 of them illustrated, online at the start of 2012. There is also a "Highlights" database with longer entries on over 4,000 objects, and several specialised online research catalogues and online journals (all free to access). In 2013 the museum's website received 19.5 millions visits, an increase of 47% from the previous year.
In 2013 the museum received a record 6.7 million visitors, an increase of 20% from the previous year. Popular exhibitions including "Life and Death in Pompeii and Herculaneum" and "Ice Age Art" are credited with helping fuel the increase in visitors. Plans were announced in September 2014 to recreate the entire building along with all exhibits in the video game Minecraft in conjunction with members of the public.
Governance
The British Museum is a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport through a three-year funding agreement. Its head is the Director. The British Museum was run from its inception by a 'Principal Librarian' (when the book collections were still part of the Museum), a role that was renamed 'Director and Principal Librarian' in 1898, and 'Director' in 1973 (on the separation of the British Library).
A board of 25 trustees (with the Director as their accounting officer for the purposes of reporting to Government) is responsible for the general management and control of the Museum, in accordance with the British Museum Act 1963 and the Museums and Galleries Act 1992. Prior to the 1963 Act, it was chaired by the Archbishop of Canterbury, the Lord Chancellor and the Speaker of the House of Commons. The board was formed on the Museum's inception to hold its collections in trust for the nation without actually owning them themselves, and now fulfil a mainly advisory role. Trustee appointments are governed by the regulatory framework set out in the code of practice on public appointments issued by the Office of the Commissioner for Public Appointments.