Great! I'd like to visit it one day!
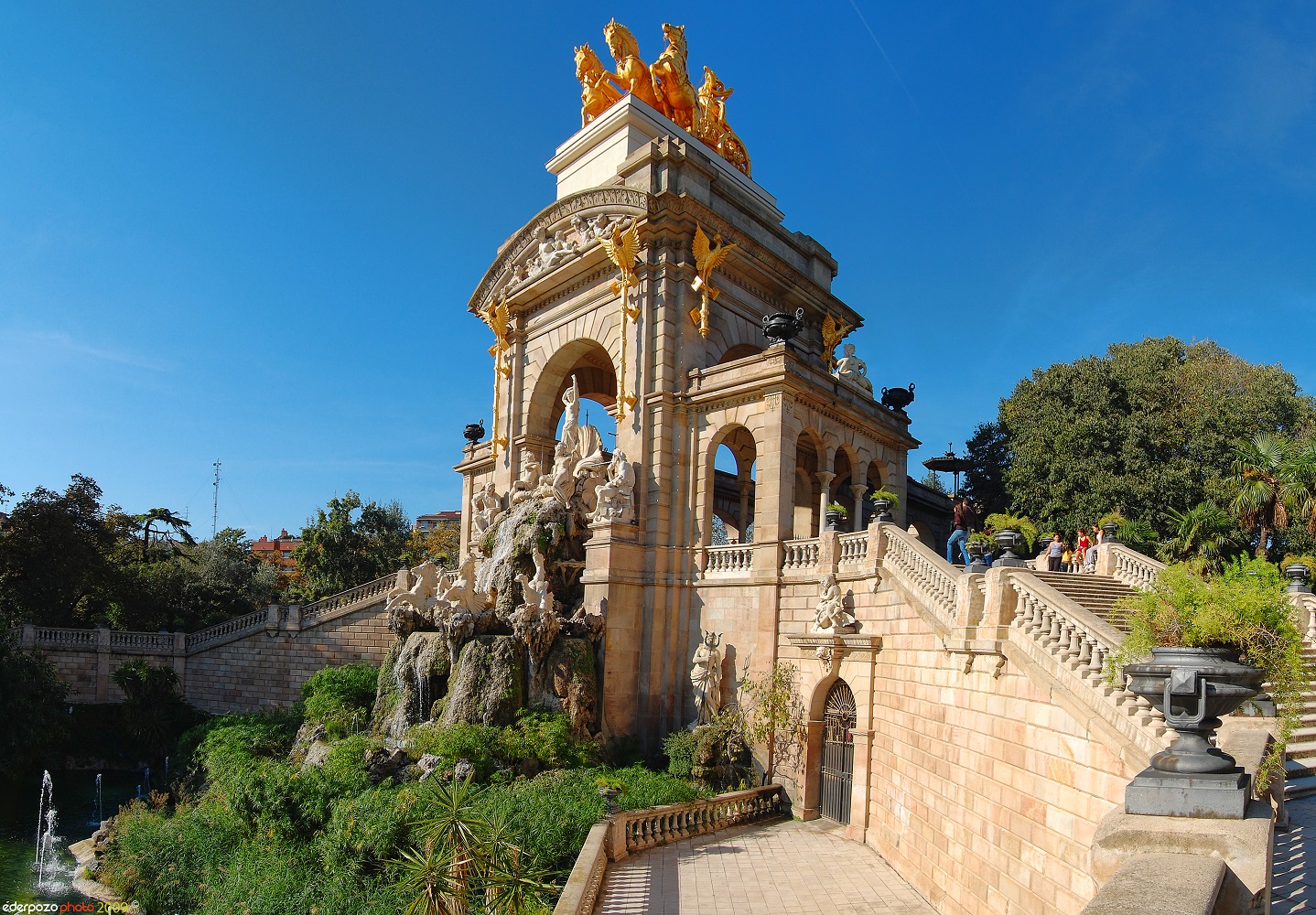
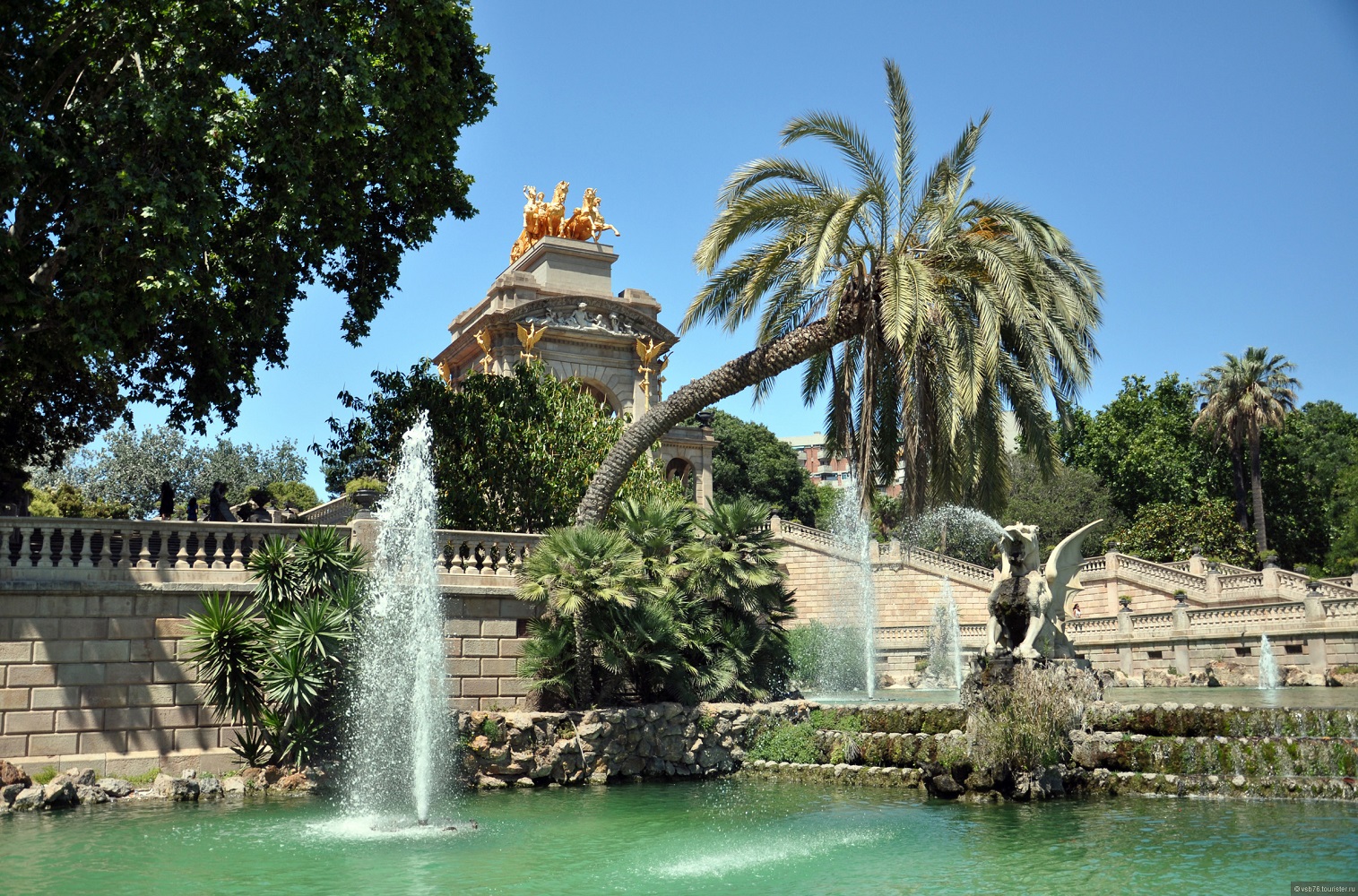
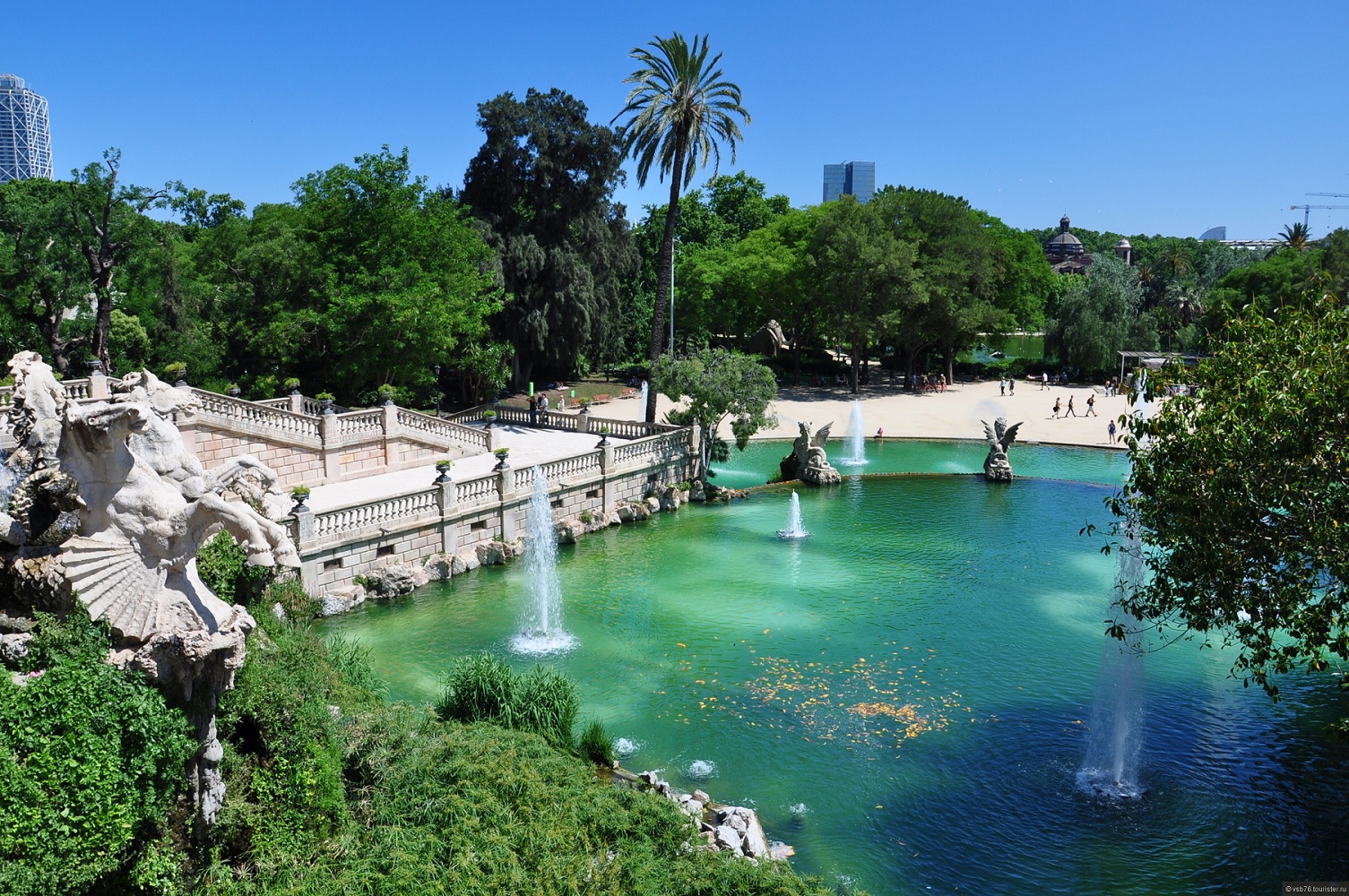
The Parc de la Ciutadella is a park on the northeastern edge of Ciutat Vella, Barcelona, Catalonia. For decades following its creation in the mid-19th century, this park was the city's only green space. The 70 acres (280,000 m2) grounds include the city zoo (once home to the albino gorilla Snowflake, who died in 2004), the Parliament of Catalonia, a small lake, museums, and a large fountain designed by Josep Fontserè (with possible contributions by the young Antoni Gaudí).
The main attraction was, from its establishment, the zoo. This was due to out of the 7,000 animals present. Near the zoo's entrance, a climbable gigantic stone mammoth is to be seen, as is a metallic cat in another area of the park.
One half of the park's paths are sinuous and rather natural seeming trails, and the other half ordered and parallel. Along both, huge a variety of vegetation is displayed.
In 1714, after a 13-month siege (War of the Spanish Succession), Barcelona fell to the army of Philip V of Spain. In order to maintain control over the city, and to prevent the Catalans from rebelling as they had in the previous century, King Philip V built the citadel of Barcelona, at that time the largest fortress in Europe.
A substantial part of the district it was constructed in (La Ribera) was destroyed to obtain the necessary space, leaving its inhabitants homeless. The fortress was characterized by having five corners, which gave the citadel defensive power, and by a rather wide surrounding margin, serving as location for the army's cannons. It included enough buildings to house 8,000 people.
Hundreds of Catalonians were forced to work on the construction for three years, while the rest of the city provided financial backing for this and for warfare-related expenses as well, with a new tax named el cadestre. Three decades later a quarter was rebuilt around the fortress named Barceloneta, which is located inside the neighborhood Ciutat Vella.
In 1841 the city's authorities decided to destroy the fortress, which was hated by Barcelona's citizens. Yet two years later, in 1843, under the regime of Maria Cristina, the citadel was restored. In 1848, after Maria Cristina's abdication and as the citadel lost its use, General Espartero razed most of the buildings within the fortress as well as its walls by bombarding it from the nearby mountain fortress Montjuic, which helped him gain political popularity. By 1869, as the political climate liberalised enough to permit it, General Prim decided to turn over what was left of the fortress to the city and some buildings were demolished under Catalan orders, for it was viewed as by the citizens as a much-hated symbol of central Spanish government.
The chapel (now the Military Parish Church of Barcelona), the Governor's palace (now Verdaguer Secondary School), and the arsenal (which is now home to the Catalan Parliament) remain, with the rest of the site being turned into the park of the citadel as we now know it, on the grounds of the former fortress, as work by the architect Josep Fontsére in 1872. Nineteen years later, in 1888, Barcelona held the Exposición Universal de Barcelona extravaganza, inspired by Mayor Rius i Taulet, and the park was redesigned with the addition of sculptures and other complementary works of art. This marked the conclusion of the old provincial and unprogressive Barcelona and the establishment of a modern cosmopolitan city. From that point until 1892, half of the park's layout was yet again enhanced, in order to obtain sufficient space for the zoo.











 Maksim Baykov
Maksim Baykov