Bute (/ˈbjuːt/; also known as the Isle of Bute, Scottish Gaelic: Eilean Bhòid or Eilean Bhòdach) is an island in the Firth of Clyde in Scotland. It is divided into highland and lowland areas by the Highland Boundary Fault. Formerly a constituent island of the larger County of Bute, it is now part of the council area of Argyll and Bute. Bute's resident population was 6,498 in 2011, a decline of just over 10% from the figure of 7,228 recorded in 2001 against a background of Scottish island populations as a whole growing by 4% to 103,702 for the same period.
Bute lies in the Firth of Clyde. The only town on the island, Rothesay, (NS087645) is linked by ferry to the mainland. Hamlets
on the island include Kilchattan Bay, Kingarth and Port Bannatyne.
Bute is divided in two by the Highland Boundary Fault. North of the fault the island is hilly and largely uncultivated with extensive areas of forestry. The highest hill is Kames Hill at 267 metres. To the south of the fault the terrain is smoother and highly cultivated although in the far south is to be found the island's most rugged terrain around Glen Callum. Loch Fad is Bute's largest body of freshwater and runs along the fault line.
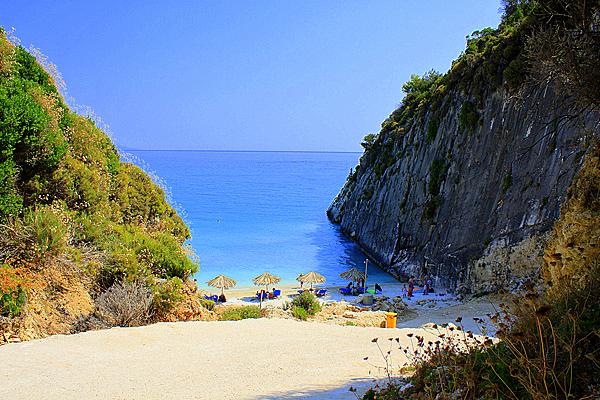
The western side of Bute is known for its beaches, many of which enjoy fine views over the Sound of Bute towards Arran and Bute's smaller satellite island Inchmarnock. Villages on the western side of the island include Straad, around St. Ninian's Bay, and Kildavanan on Ettrick Bay.
In the north, Bute is separated from the Cowal peninsula by the Kyles of Bute. The northern part of the island is sparsely populated, and the ferry terminal at Rhubodach connects the island to the mainland at Colintraive by the smaller of the island's two ferries. The crossing is one of the shortest, less than 300 metres (330 yd), and takes only a few minutes but is busy because many tourists prefer the scenic route to the island.
North Bute forms part of the Kyles of Bute National Scenic Area, one of 40 in Scotland.
History
The human occupation of Bute dates from prehistoric times. The Queen of the Inch necklace is an article of jewellery made of jet found in a cist that dates from circa 2000 BC.
Bute was absorbed into the Cenél Comgall of Dál Riata and colonised by Gaelic peoples. The island subsequently fell under Norse control and formed part of the Kingdom of the Isles, ruled by the Crovan dynasty. The Irish Text Martyrology of Tallaght makes a reference to Blane, the Bishop of Kingarth on Bute, "in Gall-Ghàidheil". However, in the 12th century, the island fell under the control of Somerled, Lord of Argyll, and possibly his Clann Somhairle descendants. At about the turn of the 13th century, Bute appears to have come into possession of the family of the Steward of Scotland, during a time of internal strife amongst Somerled's descendants.
In 1549, Dean Monro wrote of "Buitt" that it was:
very fertyle ground, namelie for aitts, with twa strenthes; the ane is the round castle of Buitt, callit Rosay of the auld, and Borrowstone about it callit Buitt. Before the town and castle is ane bay of sea, quhilk is a gude heavin for ships to ly upon ankers. That uther castle is callit the castle of Kames, quhilk Kames in Erishe is alsmeikle as to say in English the bay Castle. In this ile ther is twa paroche kirks, that ane southe callit the kirk of Bride, the uther northe in the Borrowstone of Buitt, with twa chappells, ane of them above the towne of Buitt, the uther under the forsaid castle of Kames.
Bute played a major role during World War II, and its naval involvements were especially significant. HMS Cyclops was the depot ship for the 7th Submarine Flotilla and was home-based in Rothesay Bay. A few miles further north at Port Bannatyne the luxury 88-bedroomed Kyles Hydro Hotel, overlooking the Port, was requisitioned by the Admiralty to serve as the HQ for midget submarine (x-craft) operations. In particular, it was from here (hotel renamed HMS Varbel) that the top secret and audacious attack on the Tirpitz was masterminded. Much of the training of X-Craft submariners was undertaken in the waters around Bute, and especially in the secluded waters of Loch Striven to the north of Port Bannatyne. Bute at War. Bute accommodated many officers and NCOs of the Polish Armed Forces in the West. Officially a military camp, it was unofficially thought of as a prison for Władysław Sikorski's political enemies.
Attractions
Architectural attractions on the island include the ruined 12th century St Blane's Chapel on a site associated with Saint Catan and Saint Blane, who was born on Bute. Another ruined chapel, dating from the 6th century, lies at St Ninian's Point.
The eccentric Mount Stuart House is often cited as one of the world's most impressive neo-Gothic mansions, bringing many architectural students from Glasgow on day trips. The third Marquess had a passion for art, astrology, mysticism and religion and the house reflects this in the architecture, furnishings and art collection. There is a marble chapel, much stained glass and walls of paintings. The house is open at Easter and from May to October. There are gardens with plants imported from many parts of the world, and a visitor centre. The gardens host a number of events throughout the year starting with an Easter Parade. In 2003 the fashion designer Stella McCartney married in the chapel, generating intense media interest. Activities and workshops are often held there in the summer by a local organisation that provides after school clubs and activities in the school holidays; there is also a farmers' market and a Christmas market held in the house and in the visitor centre.
The Pavilion is a 1930s edifice housing a concert hall, workshops and cafe, and is noted for its architecture. The Pavilion is little changed from when it was built.
Rothesay Castle was built 800 years ago by the hereditary High Steward of Scotland.
Ascog Hall Fernery and Gardens are a renovated Victorian residence and glass-house containing shrubs and plants from all over the Empire, including a fern believed to be over 1,000 years old.
Loch Fad is a deep freshwater loch stocked with pike and brown trout, and is available to visiting tourist fishermen. Boats are available to hire.
The Old Post Office, now used only for sorting mail, is an historic working post office (open mornings only) which houses artefacts of the early post, some from before the advent of the postage stamp.
Scalpsie Bay has a colony of over 200 seals on its beach, which can only be reached on foot across the fields. The island also has many herds of deer, rich bird life and some large hares. Wild goats with large curled horns may be seen in the north of the island.
Port Bannatyne, a village towards the north of the island, is the centre for sailing and sea-fishing on the island. It has two boatyards and a marina for 200 vessels. Langoustines are fished with creels anchored in the bay. X-Class midget submarines were stationed in Kames Bay during World War II and there is a memorial to World War II dead. Port Bannatyne Golf Club is known for scenic views from the course.
A road from Port Bannatyne goes seven miles along the shore of the Kyles of Bute to the small ferry to Colintraive on the Argyll mainland.
The 1920s Winter Gardens (now the "Discovery Centre") close to the Rothesay Pier houses a small cinema and tourist information office. Nearby are the Victorian toilets.
There are a variety of music, folk and poetry festivals, and walking trails and new cycling routes. There are some remote Bronze Age stone circles, an Iron Age fortified village, and early Christian remains (including St. Blane's Chapel). The Bute Museum of the island's history is situated behind Rothesay Castle.