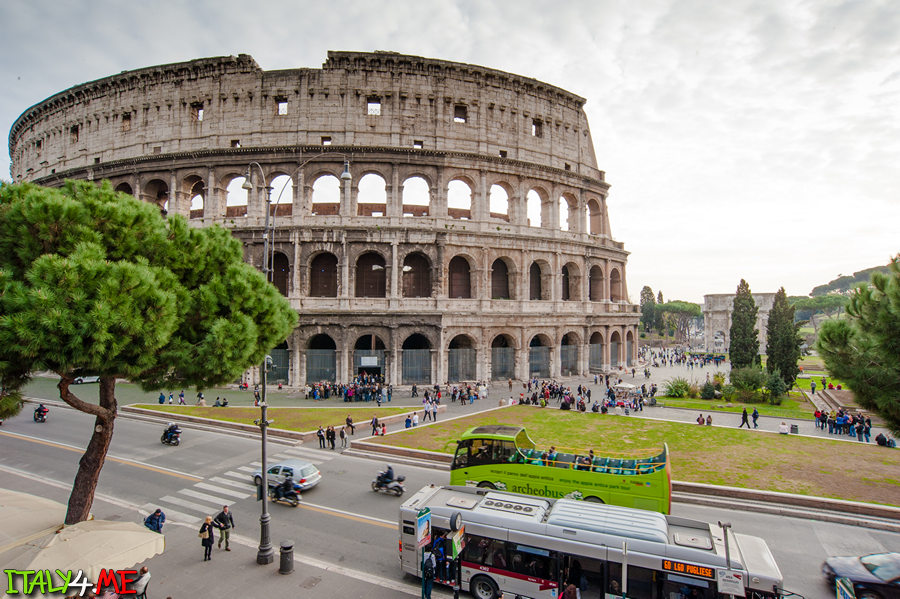
The Colosseum or Coliseum, also known as the Flavian Amphitheatre (/kɒləˈsiːəm/ kol-ə-see-əm; Latin: Amphitheatrum Flavium; Italian: Anfiteatro Flavio [anfiteˈatro ˈflavjo] [äɱːfit̪eˈäːt̪ro ˈfläːvjo] or Colosseo [kolosˈsɛo] [koloˈs̪ːɛːo]), is an elliptical amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy. Built of concrete and stone it is the largest amphitheatre ever built and is considered one of the greatest works of architecture and engineering.
The Colosseum is situated just east of the Roman Forum. Construction began under the emperor Vespasian in 72 AD, and was completed in 80 AD under his successor and heir Titus. Further modifications were made during the reign of Domitian (81–96).These three emperors are known as the Flavian dynasty, and the amphitheatre was named in Latin for its association with their family name (Flavius).
The Colosseum could hold, it is estimated, between 50,000 and 80,000 spectators, having an average audience of some 65,000; it was used for gladiatorial contests and public spectacles such as mock sea battles, animal hunts, executions, re-enactments of famous battles, and dramas based on Classical mythology. The building ceased to be used for entertainment in the early medieval era. It was later reused for such purposes as housing, workshops, quarters for a religious order, a fortress, a quarry, and a Christian shrine.
Although in the 21st century it stays partially ruined because of damage caused by devastating earthquakes and stone-robbers, the Colosseum is an iconic symbol of Imperial Rome. It is one of Rome's most popular tourist attractions and has close connections with the Roman Catholic Church, as each Good Friday the Pope leads a torchlit "Way of the Cross" procession that starts in the area around the Colosseum.
Construction, inaguration, and Roman renovations
Sestertius of Titus celebrating the inauguration of the Colosseum (minted 80 AD).
A map of central Rome during the Roman Empire, with the Colosseum at the upper right corner
The site chosen was a flat area on the floor of a low valley between the Caelian, Esquiline and Palatine Hills, through which a canalised stream ran. By the 2nd century BC the area was densely inhabited. It was devastated by the Great Fire of Rome in AD 64, following which Nero seized much of the area to add to his personal domain. He built the grandiose Domus Aurea on the site, in front of which he created an artificial lake surrounded by pavilions, gardens and porticoes. The existing Aqua Claudia aqueduct was extended to supply water to the area and the gigantic bronze Colossus of Nero was set up nearby at the entrance to the Domus Aurea.
Cross-section from the Lexikon der gesamten Technik (1904)
Although the Colossus was preserved, much of the Domus Aurea was torn down. The lake was filled in and the land reused as the location for the new Flavian Amphitheatre. Gladiatorial schools and other support buildings were constructed nearby within the former grounds of the Domus Aurea. Vespasian's decision to build the Colosseum on the site of Nero's lake can be seen as a populist gesture of returning to the people an area of the city which Nero had appropriated for his own use. In contrast to many other amphitheatres, which were located on the outskirts of a city, the Colosseum was constructed in the city centre; in effect, placing it both symbolically and precisely at the heart of Rome.
Construction was funded by the opulent spoils taken from the Jewish Temple after the Great Jewish Revolt in 70 AD led to the Siege of Jerusalem. According to a reconstructed inscription found on the site, "the emperor Vespasian ordered this new amphitheatre to be erected from his general's share of the booty." Along with the spoils, estimated 100,000 Jewish prisoners were brought back to Rome after the war, and many contributed to the massive workforce needed for construction. The slaves undertook manual labor such as working in the quarries at Tivoli where the travertine was quarried, along with lifting and transporting the quarried stones 20 miles from Tivoli to Rome. Along with this free source of unskilled labor, teams of professional Roman builders, engineers, artists, painters and decorators undertook the more specialized tasks necessary for building the Colosseum.
Construction of the Colosseum began under the rule of Vespasian in around 70–72 AD (73-75 AD according to some sources) The Colosseum had been completed up to the third story by the time of Vespasian's death in 79. The top level was finished by his son, Titus, in 80,[5] and the inaugural games where held in A.D. 80 or 81.Dio Cassius recounts that over 9,000 wild animals were killed during the inaugural games of the amphitheatre. Commemorative coinage was issued celebrating the inauguration. The building was remodelled further under Vespasian's younger son, the newly designated Emperor Domitian, who constructed the hypogeum, a series of underground tunnels used to house animals and slaves. He also added a gallery to the top of the Colosseum to increase its seating capacity.
In 217, the Colosseum was badly damaged by a major fire (caused by lightning, according to Dio Cassius) which destroyed the wooden upper levels of the amphitheatre's interior. It was not fully repaired until about 240 and underwent further repairs in 250 or 252 and again in 320. Gladiatorial fights are last mentioned around 435. An inscription records the restoration of various parts of the Colosseum under Theodosius II and Valentinian III (reigned 425–455), possibly to repair damage caused by a major earthquake in 443; more work followed in 484and 508. The arena continued to be used for contests well into the 6th century. Animal hunts continued until at least 523, when Anicius Maximus celebrated his consulship with some venationes, criticised by King Theodoric the Great for their high cost.