The Mississippi River is the chief river of the second-largest drainage system on the North American continent, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system.[10][11] Flowing entirely in the United States (although its drainage basin reaches into Canada), it rises in northern Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for 2,320 miles (3,730 km)[11] to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 31 U.S. states and 2 Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian Mountains. The Mississippi ranks as the fourth-longest and fifteenth-largest river in the world by discharge. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana.
Native Americans long lived along the Mississippi River and its tributaries. Most were hunter-gatherers, but some, such as the Mound Builders, formed prolific agricultural societies. The arrival of Europeans in the 16th century changed the native way of life as first explorers, then settlers, ventured into the basin in increasing numbers. The river served first as a barrier, forming borders for New Spain, New France, and the early United States, and then as a vital transportation artery and communications link. In the 19th century, during the height of the ideology of manifest destiny, the Mississippi and several western tributaries, most notably the Missouri, formed pathways for the western expansion of the United States.
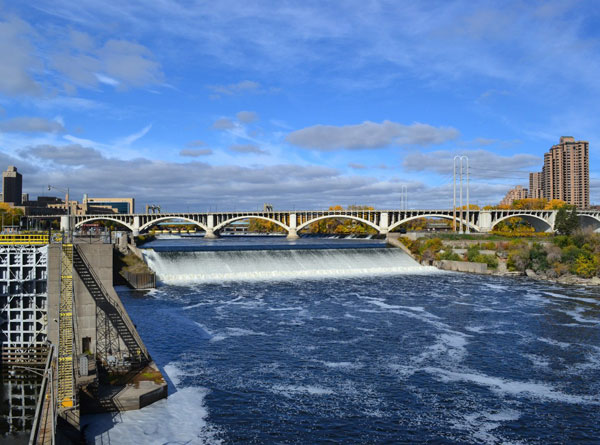
Formed from thick layers of the river's silt deposits, the Mississippi embayment is one of the most fertile agricultural regions of the country, which resulted in the river's storied steamboat era. During the American Civil War, the Mississippi's capture by Union forces marked a turning point towards victory due to the river's importance as a route of trade and travel, not least to the Confederacy. Because of substantial growth of cities and the larger ships and barges that supplanted riverboats, the first decades of the 20th century saw the construction of massive engineering works such as levees, locks and dams, often built in combination.
Since modern development of the basin began, the Mississippi has also seen its share of pollution and environmental problems – most notably large volumes of agricultural runoff, which has led to the Gulf of Mexico dead zone off the Delta. In recent years, the river has shown a steady shift towards the Atchafalaya River channel in the Delta; a course change would be an economic disaster for the port city of New Orleans.