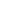
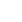
Timgad (called Thamugas or Thamugadi in old Berber) was a Roman colonial town in the Aurès Mountains of Algeria, founded by the Emperor Trajan around AD 100. The full name of the town was Colonia Marciana Ulpia Traiana Thamugadi. Trajan commemorated the city after his mother Marcia, father Marcus Ulpius Traianus and his eldest sister Ulpia Marciana.
Located in modern-day Algeria, about 35 km east of the town of Batna, the ruins are noteworthy for representing one of the best extant examples of the grid plan as used in Roman city planning.
The city was founded ex nihilo as a military colony by the emperor Trajan around AD 100. It was intended to serve primarily as a bastion against the Berbers in the nearby Aures Mountains. It was originally populated largely by Parthian veterans of the Roman army who were granted lands in return for years of service.
The city enjoyed a peaceful existence for the first several hundred years and became a center of Christian activity starting in the 3rd century, and a Donatist center in the 4th century.
In the 5th century, the city was sacked by the Vandals before falling into decline. In AD 535 the Byzantine general Solomon found the city empty when he came to occupy it. In the following century, the city was briefly repopulated as a primarily Christian city before being sacked by Berbers in the 5th century. During the Christian period, Timgad was a bishopric which became renowned at the end of the 4th century when Bishop Optat became the spokesman for the Donatist heresy. The city saw a revival of activity after the Byzantine reconquest in the 6th century, but the Arab invasion brought about the destruction of Thamugadi, where occupation ceased definitively after the 8th century.
Because no new settlements were founded on the site after the 7th century, the town was partially preserved under sand up to a depth of approximately one meter. The encroachment of the Sahara on the ruins was the principal reason why the town is so well preserved.
After the Arab sacking in the 8th century the city disappeared from history until its excavation in 1881.